
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The Key Cybersecurity Best Practices You Need to Know
88% of companies now consider cybersecurity a business risk rather than an IT problem. From that, it’s clear that the rising number of cyber-attacks globally cannot be ignored by executives.
It is no longer enough to implement basic security measures. Organizations must take a proactive approach to protect their digital assets from cyber threats. This is where the NIST Cybersecurity Framework comes in to provide a structured and flexible approach to managing cybersecurity risks.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a set of guidelines developed by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks as part of their wider goals to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness.
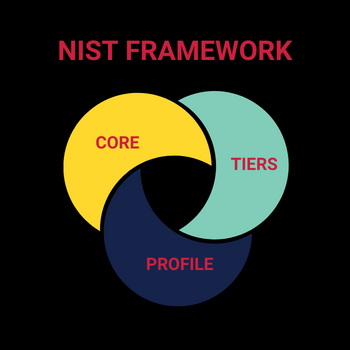
These elements represent the fundamental activities that an organization should undertake to improve its cybersecurity.
Organizations are not legally obligated to adopt the NIST framework. However, it is highly recommended – with 70% of organizations viewing NIST’s framework as a security best practice.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Elements
The first element of the NIST cybersecurity framework is the five core functions: identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover.
5 Core Functions of the Nist Cybersecurity Framework
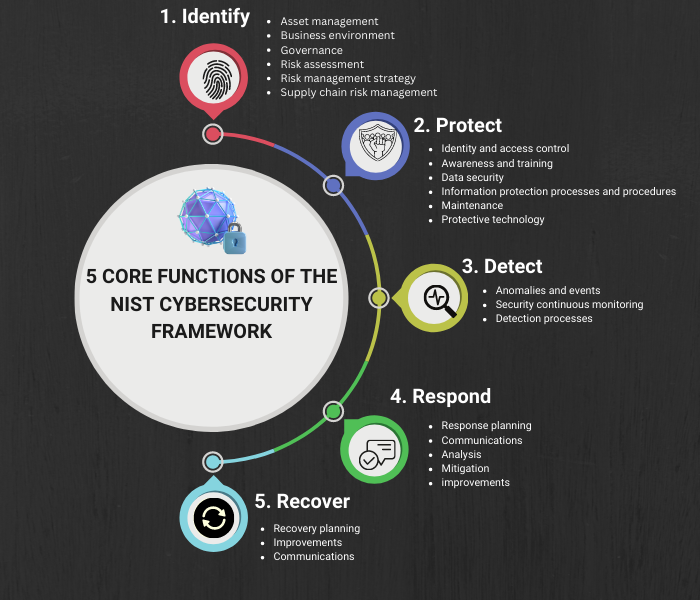
1. Identify
The first component is all about identifying and understanding the assets, data, and systems that need to be protected, as well as the potential threats and vulnerabilities they face.
This is achieved by conducting risk assessments, taking inventory of hardware and software assets, and defining data classifications.
Each core function also contains subcategories. For example, within identity the focus areas are:
- Asset management
- Business environment
- Governance
- Risk assessment
- Risk management strategy
- Supply chain risk management
2. Protect
The second component focuses on implementing safeguards and controls to protect against any potential cyber threats that were identified in the first core function.
This involves developing and implementing security policies like zero trust, conducting employee training, and implementing security measures such as identity and access controls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and other security technologies.
The focus areas here are:
- Identity and access control
- Awareness and training
- Data security
- Information protection processes and procedures
- Maintenance
- Protective technology
3. Detect
The third component involves detecting cybersecurity events and incidents as quickly as possible.
IBM reported that the average time to identify a breach in 2021 was 212 days. Anything to improve this number could have a significant impact on reducing the financial and reputation losses caused by cybersecurity breaches.
This requires monitoring and detection systems, the adoption of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity, conducting vulnerability assessments, and red-team penetration testing.
Red-team in cybersecurity refers to a team of ethical hackers that attempt to exploit an organization’s weaknesses to raise awareness of any areas that may be susceptible to future breaches.
The focus areas here are:
- Anomalies and events
- Security continuous monitoring
- Detection processes
4. Respond
The fourth component involves responding to any cybersecurity incidents and data breaches in a timely, effective, and cost-efficient manner.
The average cost of a data breach in 2021 was $4.24 million. So, responding to cybersecurity incidents as quickly and as effectively as possible could reduce this number significantly.
This involves establishing a clear and comprehensive incident response plan, conducting regular drills and exercises, and providing appropriate guidance and support to affected stakeholders.
The focus areas here are:
- Response planning
- Communications
- Analysis
- Mitigation
- improvements
5. Recover
The final component is all about the worst-case scenario. How do you recover from a cybersecurity incident and restore normal operations?
This includes developing and implementing business continuity and disaster recovery plans, conducting post-incident reviews, and continuously improving the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
The focus areas here are:
- Recovery planning
- Improvements
- Communications
Each of these components is designed to work cohesively together with the ultimate goal of providing a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity risk management.
By implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, organizations can better:
- Identify and understand their cybersecurity risks
- Protect against potential cyber threats
- Detect incidents in a timely manner
- Respond more effectively to incidents in the event they do occur
- Recover from cyber attacks at a quicker rate
Implementation Tiers
Once you have mapped out your current cybersecurity practices and determined where improvements can be made, you can move on to implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework’s Implementation Tiers.
The tiers represent a progression from basic cybersecurity practices to more advanced and adaptive practices.
There are four implementation tiers, each with its own set of characteristics that you can use to assess where your organization currently stands.
Tier 1: Partial
Organizations that have an ad-hoc approach to cybersecurity with an inconsistent process for managing risks, fall into this tier.
Often they’ll have limited awareness of their cybersecurity risks, and their approach to cybersecurity is reactive as opposed to proactive.
Tier 2: Risk-Informed
Organizations that have begun to develop a risk management process for their cybersecurity practices fall into this tier.
They generally have a better understanding of their cybersecurity risks and have implemented some cybersecurity practices.
However, they may still be missing a formalized cybersecurity risk management process, and their cybersecurity practices may not be fully integrated into their overall organizational processes.
Tier 3: Repeatable
Organizations that have a formalized cybersecurity risk management process that is integrated into their overall organizational processes, fall into this tier.
These organizations have implemented a range of cybersecurity practices and are working towards a proactive approach to their cybersecurity efforts.
Generally, they have a good understanding of their cybersecurity risks and are continuously monitoring and improving their cybersecurity practices.
Tier 4: Adaptive
Organizations that have an advanced and proactive approach to cybersecurity, fall into this tier.
Organizations in this tier are constantly monitoring their cybersecurity risks and adapting their cybersecurity practices to address new and emerging threats.
They have a strong cybersecurity risk management process that is fully integrated into their overall organizational processes. Overall, the implementation tiers are used as a roadmap to improve an organization’s cybersecurity practices and move towards a more proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity.
Profiles
Profiles are a key component of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework.
They’re used to identify opportunities for improving an organization’s cybersecurity by comparing the “current” profile against a “target” profile to establish the existing and desired state of their cybersecurity program.
The NIST framework is voluntary so there is no right or wrong way to select which of the five core functions and subcategories to focus on. Organizations can map out your cybersecurity requirements, mission objectives, and operating methodologies that act as your target-state profile.
Then map out the organization’s current practices against the subcategories of the Framework Core functions. This is what’s referred to as the current-state profile.
By comparing the current cybersecurity activities to the objectives and requirements outlined in the target profile, an organization can identify gaps and determine a roadmap that prioritizes efforts and improvements accordingly.
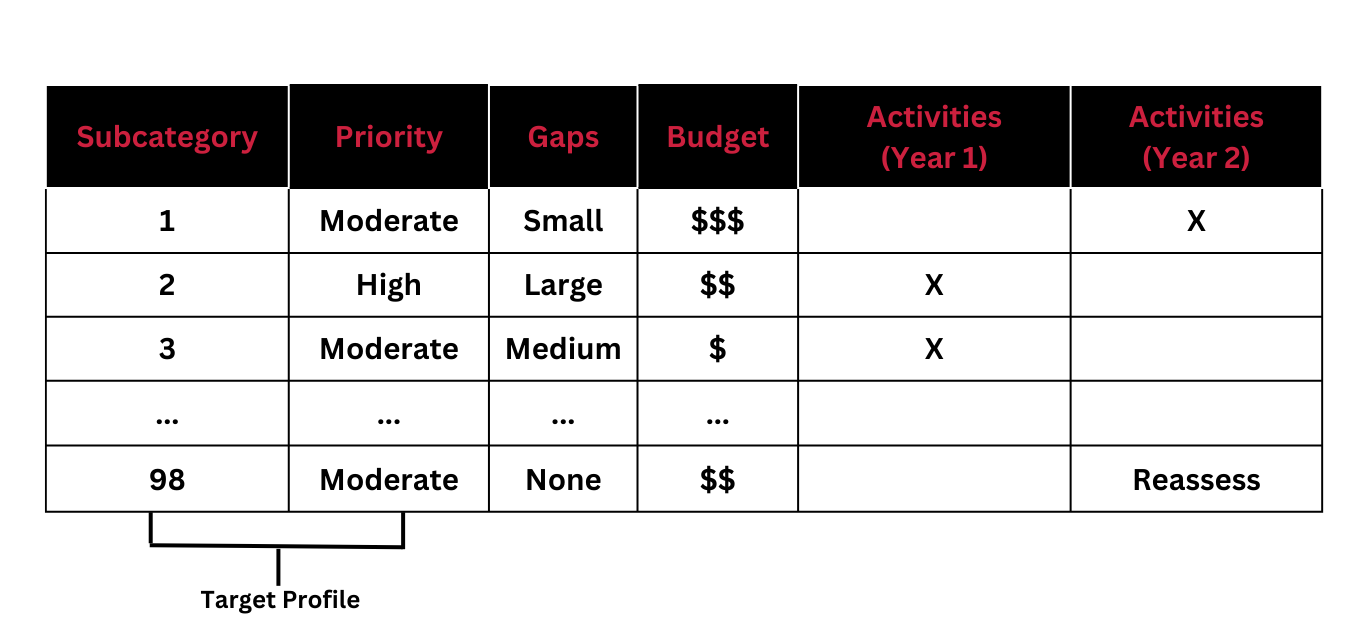
Profiles can be shared with stakeholders, including customers, partners, and regulators, to demonstrate an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity and its progress in managing cybersecurity risks.
Benefits of Implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Successful implementation of the NIST cybersecurity framework has numerous benefits for any organization.
One benefit is that it provides a common language for communication between different departments and stakeholders within the organization. This shared language helps break down silos and promote collaboration between departments, which is critical for an effective cybersecurity program.
The framework also provides a structured approach to managing cyber risk. This helps organizations prioritize their efforts and resources more effectively by identifying the most critical assets and the risks that threaten them.
Another benefit of implementing the NIST framework is that it helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements. The framework is designed to be flexible and adaptable to different regulatory environments, while also helping organizations demonstrate compliance with a variety of cybersecurity regulations and standards.
Finally, implementing the NIST framework can help organizations build trust with their customers and partners. Demonstrating a structured and comprehensive approach to managing cyber risks shows how committed they are to protecting customer data and privacy.
Who Is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework For?
It’s clear that the NIST framework is an excellent tool for strengthening your cybersecurity posture. But who exactly is it for?
In short, the framework is designed for any and all organizations that want to improve their cybersecurity practices, regardless of size or industry.
Small businesses can benefit from using the framework to identify and address cybersecurity risks to then implement best practices to safeguard their operations.
On the other hand, large enterprises can use the framework to help them align their cybersecurity practices with their overall business goals and objectives.
The NIST cybersecurity framework is excellent for government agencies and organizations in regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and banking.
Complying with industry-specific regulations and standards is critical in these sectors – the NIST framework helps meet these regulations and standards whilst also improving their overall cybersecurity efforts.
