The Last Mile of AI: Specialized Architectures for Real-Time Inference and Global Delivery

The Last Mile of AI: Specialized Architectures for Real-Time Inference and Global Delivery
I. Introduction: The Pivot from Training to Deployment
In our previous three installments, we architected the AI Factory for velocity: securing the power baseload, managing the thermal cliff with liquid cooling, and eliminating bottlenecks with lossless fabric and CXL memory. Now, we face the final and most pervasive challenge: Inference.
The architectural goals shift entirely:
-
Training optimizes for Time-to-Train and Throughput (total gradients processed).
-
Inference optimizes for Latency (time per query, measured in milliseconds) and Cost-per-Query.
This is the 90/10 Rule: Training is the massive, one-time investment (10% of operational time), but inference is the continuous, real-time workload (90% of the compute and energy consumption) that determines user experience and profitability. The inference data center is not a training cluster; it is a global, low-latency, and highly decentralized web of compute.
II. The Inference Hardware Hierarchy: Efficiency Over Raw Power
The hardware selection for inference is driven by efficiency; maximizing inferences per watt, not just raw performance.
A. Specialized Accelerators for the Forward Pass
The core task of inference is the forward pass (a single, continuous calculation), which is far less demanding than the backpropagation required for training.
-
The GPU Role: High-end GPUs (like the NVIDIA H100) are still used for the largest Generative AI (GenAI) models, particularly when large sequence lengths or high token generation rates are needed. However, their raw power is often overkill for smaller models or specific tasks.
-
The Cost/Power Advantage (The State of the Art): The market is rapidly moving towards silicon optimized solely for serving:
-
Dedicated ASICs: Chips like AWS Inferentia, Google TPU Inference Cores, and Meta MTIA are designed to offer peak performance and dramatically better power efficiency for fixed models, often achieving a much lower Cost-per-Query than general-purpose GPUs.
-
FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays): FPGAs offer high performance per watt and are favored where workloads change frequently (reconfigurability) or when extreme low-latency processing is required for specific algorithms (e.g., real-time signal processing, as demonstrated by Microsoft Project Brainwave).
-
B. Memory and Model Storage Requirements
Inference requires significantly less VRAM than training (only enough to hold the final model weights). This constraint drives major innovations:
-
Quantization and Compression: The state of the art involves aggressive software techniques like AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) or FP8/FP4 model formats. These methods compress large LLMs down to a fraction of their original size with minimal loss in accuracy, allowing billion-parameter models to fit onto smaller, cheaper edge GPUs or even highly-optimized CPUs.
-
Low-Latency Storage: Inference systems need ultra-fast access to model weights for rapid model loading and swapping (context switching). High-speed NVMe SSDs and local caching are critical to ensuring the accelerator is never waiting for the next model to load.
III. Software Frameworks: Achieving Low Latency
Hardware is only half the battle; software frameworks define the millisecond response time that users demand.
A. The Challenge of GenAI Latency (The KV Cache)
Large Language Model (LLM) inference is fundamentally sequential (token-by-token generation). To generate the tenth token, the system must access the intermediate state from the previous nine tokens, introducing a sequential “wait” time.
-
Key-Value (KV) Caching: The most crucial software optimization is storing the calculated intermediate state for previously generated tokens (the KV Cache). This feature, which consumes significant memory, drastically reduces redundant computation, becoming the primary driver of inference speed and memory consumption.
-
PowerInfer & Model Parallelism: Cutting-edge research, demonstrated in papers like PowerInfer, focuses on splitting model computation between high-performance accelerators and lower-power CPUs, running the less computationally intensive parts of the model on the CPU to maximize efficiency and further reduce latency on consumer-grade chips.
B. Optimized Serving Frameworks (The State of the Art)
To maximize GPU utilization, requests must be served continuously, even if they arrive asynchronously.
-
Continuous Batching (vLLM / Triton): This core technique, popularized by frameworks like vLLM and NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, maximizes throughput by dynamically batching incoming requests that arrive at different times. It keeps the GPU pipeline full, minimizing idle time and maximizing throughput while maintaining the low-latency contract for each user.
-
Decentralized Orchestration: Modern model serving relies on sophisticated orchestration tools (like Kubernetes) to handle automated load balancing, health checks, and autoscaling across heterogeneous hardware deployed across the globe.

IV. Architecture for Global Delivery: The Last Mile
The inference data center is defined by its ability to defy the physical constraints of distance.
A. Geographic Placement and the Speed of Light
Latency is directly tied to the physical distance between the user and the inference compute. The speed of light is the immutable enemy of real-time AI.
-
Decentralized Deployment: For applications demanding under 10ms response times (think real-time bidding, financial trading, or voice agents), the service must be deployed at the Edge (e.g., regional POPs or 5G cell sites). The architecture shifts from centralized training superclusters to a highly decentralized web of inference nodes positioned close to the user base.
-
The Network Edge Fabric: Inference networks prioritize stable, low-jitter connections over absolute peak bandwidth. Fiber backbones, CDNs (Content Delivery Networks), and highly efficient load balancers are key to distributing traffic and ensuring real-time responsiveness without frustrating delays or network errors.
B. Cost of Ownership (TCO) in Inference
The financial success of an AI product is measured by its Total Cost per Inference.
The TCO metric changes dramatically from:
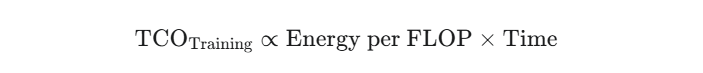
to:

This is where specialized silicon, model compression, and clever software orchestration win the cost war over millions or billions of queries.
V. Visualizing the Impact: Latency is Profit
In the world of Generative AI, every millisecond of latency has a quantifiable business impact on user engagement and revenue.
-
Conversion and Engagement: Studies have repeatedly shown that adding just 100 milliseconds of latency to a web application or API response can reduce user engagement by 7% and decrease conversion rates. For a transactional AI service, this directly translates into millions of dollars lost.
-
User Experience (UX): For conversational AI, latency is the difference between a natural, fluid conversation and a frustrating, robotic one. Low-latency inference is the primary technological component of a successful, sticky AI product.
-
The Decoupling: Training costs are fixed (amortized over the lifespan of the model), but inference costs are continuous and variable. The architectural decisions made at the deployment edge directly determine the long-term profitability and scalability of the entire AI business.
VI. Conclusion: The AI Product is Defined by Inference
The success of AI as a product relies entirely on delivering a seamless, real-time experience. This demands systems architects who are experts in algorithmic efficiency and global distribution, not just raw processing power. The inference data center is the ultimate expression of this expertise.
What’s Next in this Series
This installment completes our deep dive into the four foundational pillars of the AI Factory: Power, Cooling, Training Fabric, and Inference.
We’ve covered how to build the most powerful AI infrastructure on Earth. But what if compute shifts off-planet?
Looking Ahead: The Orbital Compute Frontier
We are tracking radical concepts like Starcloud, which plans to put GPU clusters in orbit to utilize 24/7 solar power and the vacuum of space as a heat sink. If compute shifts off-planet, AI stacks will need space-aware MLOps (link budgets, latency windows, radiation-hardened checkpoints) and ground orchestration that treats orbit as a new region. This is an early, fascinating signal for the future AI infrastructure roadmap.
Explore more from RediMinds
As we track these architectures, we’re also documenting practical lessons from deploying AI in regulated industries. See our Insights and Case Studies for sector-specific applications in healthcare, legal, defense, financial, and government.
Select Reading and Sources
Previous Installments in This Series
-
Powering AI Factories: Why Baseload Brainware Defines the Next Decade
-
The Thermal Cliff: Why 100 kW Racks Demand Liquid Cooling and AI-Driven PUE
-
The AI Nervous System: Lossless Fabrics, CXL, and the Memory Hierarchies Unlocking Trillion-Parameter Scale
Inference and Edge Architecture
-
PowerInfer: Fast LLM Serving on Consumer GPUs (arXiv 2024)
-
Our Next Generation Meta Training and Inference Accelerator (MTIA) – Meta AI Blog
-
AWS Inferentia – AI Chip Product Page
-
Project Brainwave: FPGA for Real-Time AI Inference – Microsoft Research
-
Continuous Batching and LLM Serving Optimization (vLLM / Triton)
-
Quantization and Model Compression Techniques (AWQ, FP8)
Emerging Frontiers
-
Starcloud: In-orbit AI and Space-Aware MLOps (NVIDIA Blog)
-
Vector-Centric Machine Learning Systems: A Cross-Stack Perspective (arXiv 2025)