
Zero Trust Cybersecurity – The Crucial Framework Your Company Should Implement
When it comes to cybersecurity models, there’s no need to reinvent the wheel. Designing a security system from scratch just isn’t an option for most enterprise companies – that’s why it’s common practice to pick a publicly available framework.
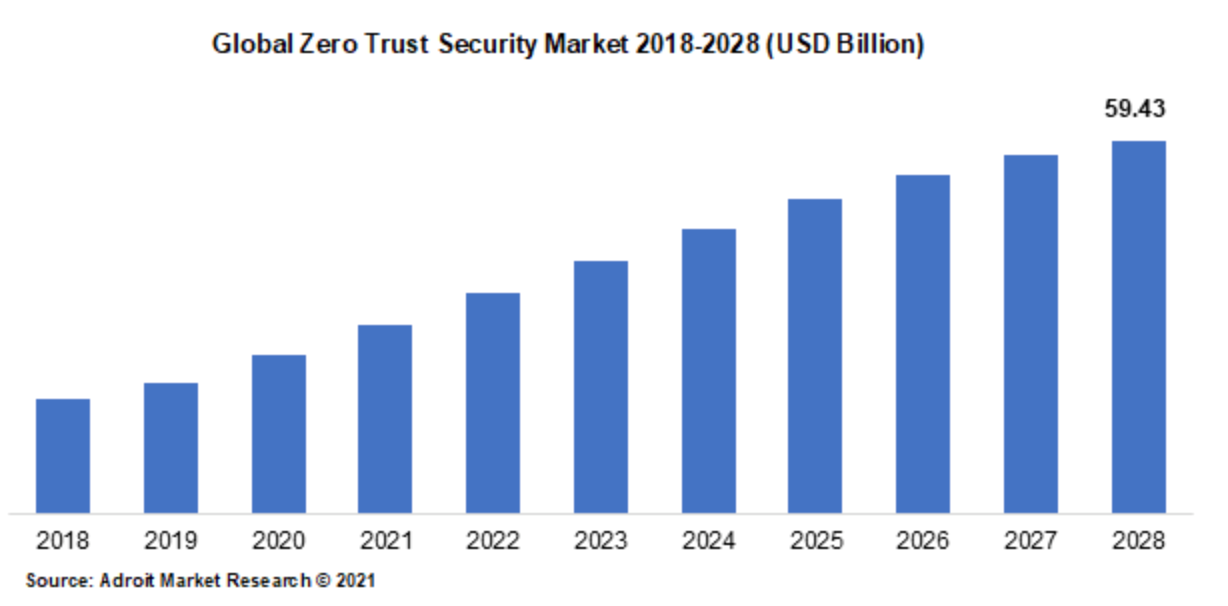
One of the most popular of which is the Zero Trust cybersecurity framework, estimated to reach a market value of 59.43 billion by 2023.
(source: Adroit Market Research)
This article will cover:
- What it is
- Why it’s important
- Threats to traditional security
- Why your business should be implementing Zero Trust
- Challenges faced with Zero Trust
- Implementing Zero Trust
What is the Zero Trust framework?
The Zero Trust security model has been around for over 10 years. But, it wasn’t until the past few years that it became clear how to implement it efficiently and cost-effectively, thus companies have only really started adopting it more recently.
The principles of zero trust are simple:
“Never trust, always verify – every request from every user, in or outside the organization must be authenticated, authorized, and encrypted in real-time”
Adopting Zero trust as an organization changes the concept of ‘perimeter’ from being location-based to identity and access-based – a concept that’s integral in today’s age of remote working, cloud computing, and hybrid storage systems.
That brings us to…
Why Is Zero Trust So Important in Today’s Digital Landscape?
The last few years have seen an exponential change in the digital landscape and thus, a significant change in how companies operate. Specifically, the shift to remote and hybrid remote working.
Such a shift has brought about increased exposure to cyber threats that were previously not even a consideration.
With more and more employees working outside of the office, users are accessing potentially critical company information and data on unsecured networks.
This, coupled with the fact that cybercriminals are becoming more and more sophisticated, forever finding new and improved ways to exploit weaknesses in an organization’s system, leaves organizations more vulnerable than ever to cyber threats.
Zero trust is an excellent way to combat these issues – by simplifying security efforts and effectively verifying user identities both before and during every user’s session. This allows for suspicious behavior to be picked up in real time.
So, it’s no surprise that Hartner captures a 60% YoY growth rate in companies adopting Zero trust.
Threats to Traditional Network Security
Cyber Attacks Becoming More Sophisticated
As technology advances, so do cybercriminal tactics. Traditional security methods like firewalls and antivirus software are no longer enough to protect you against new and more advanced threats.
In this new era of the digital landscape in which traditional security methods aren’t a match for malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks that cybercriminals are deploying today.
Increased Number of Remote Employees
With more and more employees accessing company networks from outside the office, this has created a larger attack surface for cybercriminals to target.
Many remote employees and devices may not have the same level of security as those within the office – this is what’s referred to as edge cybersecurity.
While using personal devices for work purposes can increase the risk of data breaches as they may not be as secure as company-issued devices.
An alternative solution to Zero Trust is to use a VPN. On the face of it, they work relatively well by funneling access through a private connection when accessing an unsecured connection, essentially encrypting the user’s online activity.
However, VPNs have a significant drawback versus zero trust. Because VPNs work on a policy of implicit trust for network access, in the event that just one user is compromised, the intruder gains access to the entire system.
This kind of access in the wrong hands could have catastrophic results.
Additionally, VPNs aren’t ideal for scalability on complex networks and offer no risk detection features.
Why Your Business Should Be Implementing Zero Trust
Improved Inventory of Infrastructure
For Zero Trust to work effectively, it requires an organization to have an accurate inventory of infrastructure. This means a full log of users, devices, programs, and services.
This is what allows IT teams to allocate who has access to which parts of the network. Simply put – holes in the inventory infrastructure equals holes in the organization’s cybersecurity.
Improved Data Protection
Due to the fundamental principles of zero trust, users attempting to access critical company data are subject to the identity and validation process before they are granted access.
This allows an organization to define who can be granted access and when.
Additionally, once a user gains access they are continually monitored and re-authorized. This allows for any abnormal behavior to be flagged in real-time.
The Zero Trust framework also takes advantage of micro-segmentation which involves dividing the network into smaller, more secure segments. This approach helps to reduce the attack surface of the network and minimize the impact of a successful attack.
In the event of a breach, the attacker will be limited to a smaller portion of the network, reducing the overall risk to the organization.
Increased Network Visibility
The Zero Trust framework provides a comprehensive view of all network activity.
Because all devices and users accessing the network are verified and authenticated, this generates an abundant amount of information in regard to network activity.
The resulting data logs contain who and what accessed the network, what applications and software they accessed, and for how long – visibility that helps an organization detect and respond to security threats more effectively and quickly.
The powers of machine learning can be harnessed here to augment this process and automatically detect patterns of normal behavior and more importantly, when out-of-the-ordinary activities are taking place, in real-time.
Check out our article for more on artificial intelligence in cybersecurity.
Improved Compliance With Industry Regulations
Many regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, require you to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
The Zero Trust framework provides ways to implement the requirements in a structured and consistent manner.
For example, the principle of authenticating and verifying all devices and users accessing a network complies with the regulation to secure access control.
Adopting the Zero Trust framework within your organization means that you can take advantage of advanced security tools like encryption and data loss prevention (DLP) technologies – more tools that help your organization protect sensitive data and comply with regulatory requirements.
Streamline Security Policy Creation
Traditional security measures often operate independently from one another.
This leaves parts of your organization’s infrastructure vulnerable and susceptible to cyber-attacks – and if there’s one thing cyber criminals are good at, it’s exploiting a weakness in a system.
Zero Trust helps with this as it allows for one global policy that can be created and implemented throughout the whole infrastructure.
Flexibility When Changing Technologies
As an enterprise expands and evolves, so do the business processes and technologies used – technologies like apps, data, and services.
As the Zero Trust framework isn’t tied to any one specific technology or system, when a change in technology is required, the Zero Trust security framework can be easily adapted to the new environment. The policies and controls that are put in place for securing access to resources remain consistent, regardless of the technology being used.
For example, if an enterprise decided to switch from using a traditional on-premise infrastructure to a cloud-based infrastructure, the Zero Trust framework can be applied to the new environment, allowing for a seamless and secure transition.
Challenges of Zero Trust Implementation
Integration With Existing Systems
The barrier to entry when adopting the Zero Trust security framework is largely dependent on the current infrastructure of the organization.
If your organization requires a lot of new technologies and updates for successful implementation, this of course takes time and money.
This can cause problems for organizations as they need to ensure that the new system integrates seamlessly with their existing network, applications, and security tools.
Addressing Cultural Resistance to Change
As a whole, people don’t like change. This means that the idea of adopting a new security model may result in pushback from employees.
This is why it’s critical to effectively communicate the benefits that the new security model will bring to the organization. Check out our article on employee cybersecurity training for our recommended training best practices.
Addressing Budget Constraints
As mentioned above, depending on the current infrastructure of the organization, implementing the Zero Trust framework seamlessly may require investment in new technology and tools, as well as hiring new staff, subject matter experts, or retraining existing employees.
Sometimes it can be difficult to secure key stakeholder buy-in for company improvements that don’t directly impact the bottom line of the business.
This is why the importance of money saved with increased security needs to be outlined, highlighting the risk of not getting your cybersecurity right.
This shouldn’t be too hard considering that IBM reported that the average cost of a data breach in the United States is $9.44 million.
Implementing Zero Trust
Often when people look at the Zero Trust framework, they instantly think of applying it to all applications and data sets immediately – which is a momentous task for large enterprises.
But that couldn’t be further from the truth. The Zero Trust framework can be implemented step-by-step in a gradual process.
By starting with specific applications or data sets or even types of users that the organization deems to be vulnerable assets to the business. For example, remote workers using their home or public networks.
Assessing Current Security Framework
The first step in implementing the Zero Trust framework is to take a look at the existing infrastructure.
This includes identifying any vulnerabilities, assessing the existing security systems, and understanding the current threat landscape.
This information can be used to determine what changes need to be made to the current security practices and what tools and technologies are required to effectively implement Zero Trust.
Defining the Zero Trust architecture
With a thorough assessment of current security measures and risks, you can define your Zero Trust architecture.
This involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps required to implement Zero Trust, as well as defining the policies, processes, and technologies that will be updated.
Selecting the Right Tools and Technologies
A key component of the Zero Trust model is the use of the right technologies that are best suited to your organization.
Whether you’re going to implement multi-factor authentication, passwordless authentication, encryption, security information, and event management (SIEM) systems, it’s important to take into consideration factors like cost, ease of integration, and scalability.
If your identity and access management solution isn’t fully serving your organization, get in touch with one of our experts today to discuss your best way forward to better secure your systems.
