
Cybersecurity for Enterprise: 5 Reasons Securing Your Digital Assets Should Be Your Top Priority in 2023
You may be wondering, “what kind of digital assets are you talking about?”
Well, anything from employee personal information like their social security number, date of birth, and home address, to customer information like their bank and credit card details.
Now, large enterprises like the banks have had years to fine-tune their physical security:
- High-security vaults that can only be opened at certain times of day by certain individuals
- Huge teams of security staff
- Well-thought-out contingency plans for when there is a physical threat
- Enterprise Cybersecurity Best Practices
Relatively speaking, defending digital assets against cyber criminals is a new form of security in comparison – physical money has been around for 100’s of years, the internet has only been around since 1983.
That’s why in this article, we’ll cover:
- What Is Enterprise Cybersecurity?
- Why It’s Important for Your Business
- Who Is Exceptionally Vulnerable to Cyber Attacks?
- Recent Examples of Cybersecurity Breaches
What Is Enterprise Cybersecurity?
Enterprise cybersecurity in its most simplistic form is “everything that protects a company’s digital information from falling into the wrong hands.”
This includes any data about the company, its employees, customers, or partners. Whether it be data that’s stored physically on-site, on the cloud or a combination of the two.
Why Is Enterprise Cybersecurity Important for Your Business?
As per Gartner’s 2022 study, 88% of companies now consider cybersecurity a business risk rather than an IT problem.
This is no surprise considering 96% of companies proved to be vulnerable to external attacks in a Positive Technology 2022 study.
Here are 5 reasons why cybersecurity is so important for enterprises:
- Prevents data breaches
- Slows down hackers
- Protect customer data
- Prevents reputation loss
- Prevent financial loss
1. Prevent Data Breaches
Data breaches occur when sensitive, confidential, or protected data falls into the wrong hands.
This is usually the result of a hacker breaking into the company system, an inside employee maliciously gaining access to the data, or an employee unintentionally losing or exposing the data.
In fact, 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. That’s why thorough and consistent employee cybersecurity training is highly critical to ensuring every member of your team is alert and equipped to spot cyber threats.
This, coupled with a well-executed identity and access management solution, ensures only the correct users have access to data and only when they need it, mitigating the risk of a data breach.
2. Slow Down Hackers
The goal of a hacker is to find a weakness in a system and exploit it – usually for their own financial gain.
As the old saying goes “you’re only as strong as your weakest link”.
A well-defined cybersecurity solution should of course include a proactive fraud detection and prevention solution to assess any weaknesses within the business systems in order to make them stronger. This in turn makes it more difficult for hackers to find and exploit them.
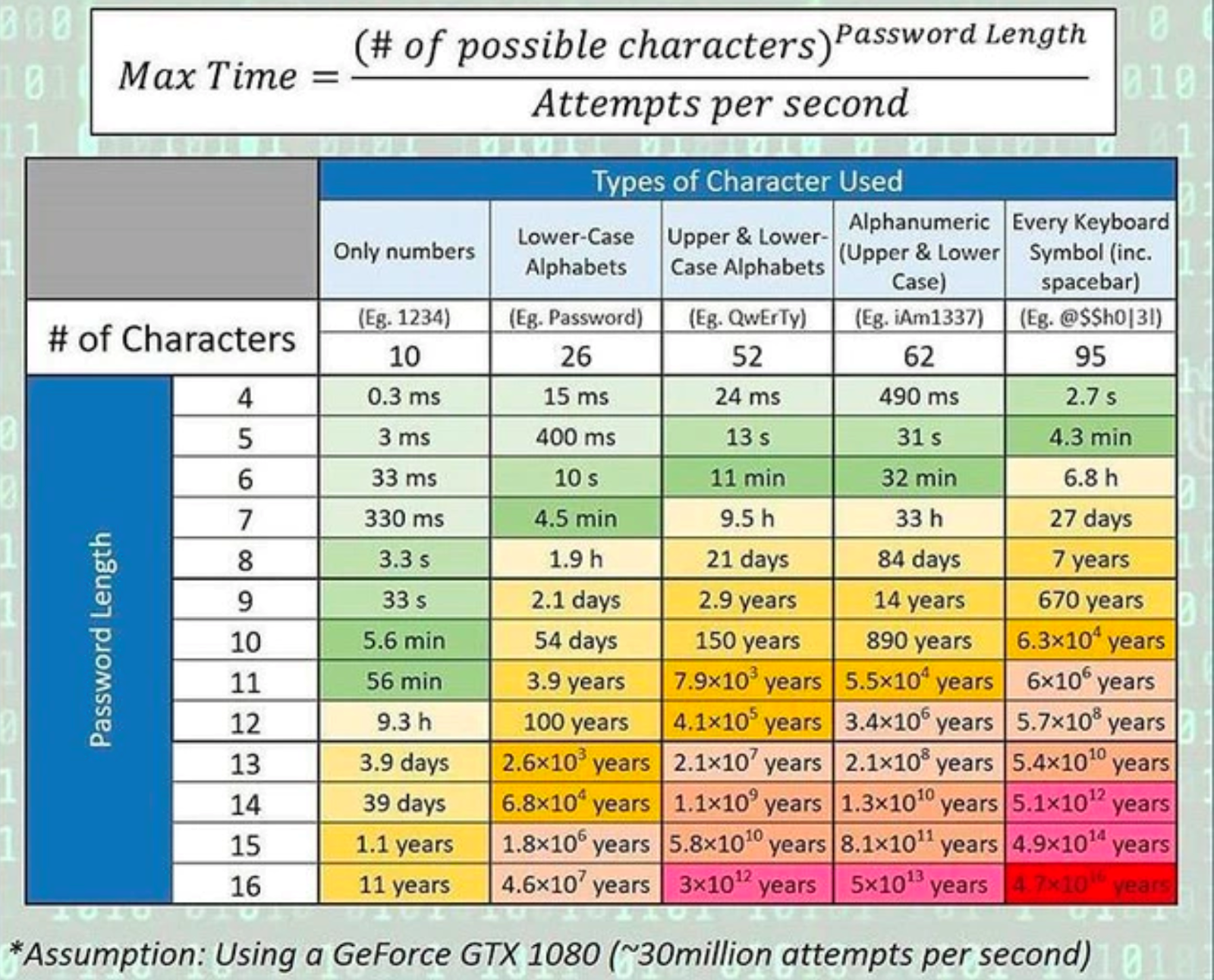
For example, just take a look at how much longer it would take a hacker using brute force tactics to guess a password of 16 characters, using every keyboard symbol (47,000,000,000,000,000 years) versus just four numbers (0.3 milliseconds).
Check out our full article on password best practices to ensure your password policies are up to scratch.
3. Protect Customer Data
Any enterprise that handles customer data has a clear responsibility to those customers to protect that data.
Customers value their privacy and generally don’t take too kindly to their data being breached. Not to mention the rules and regulations that have to be followed in order to maintain compliance with governing bodies.
The stringent EU GDPR regulations are just one example of that responsibility, but it applies and should be taken seriously across every country and industry.
The loss of customer data can be catastrophic for any enterprise – just look at the experiences of Robin Hood, which made worldwide news in 2021. They experienced a data breach in which the personal information of 7 million customers was compromised. More than 5 million customer email addresses and 2 million customer names were stolen.
The stock price of the company fell 3.8% in just 1 day following the announcement.
4. Prevent Reputation Loss
While such a huge part of our society revolves around social media – online trends, cancel culture, and both companies and individuals are under the public microscope. The online reputation of a business has never been so important.
Considering that 56% of customers now actively show an interest in a company’s cyber-resilience, it’s never been more critical to get your cybersecurity program absolutely right.
Data breaches can have a catastrophic negative effect on public opinion which leads to high customer churn, a serious hit to your bottom line, and investors scurrying to disassociate with your brand.
5. Prevent Financial Loss
The average cost of a data breach in the United States was $9.44 million in 2022 according to IBM.
Failure to follow regulations such as GDPR and CCPA may result in financial fines, and your company may be sued for mishandling customer data.
For example, in 2020 one of the largest banks in the United States had to notify more than 1.5 million customers that their social security number had been stolen in a data breach.
This resulted in the customers bringing a lawsuit against the company, costing the bank a total of $5.9 million to settle in 2021.
Who Is Exceptionally Vulnerable to Cyber Attacks?
Not all industries are created equally. Generally speaking, some industries are at greater risk of cyber attacks than others.
Naturally, the data held by companies in some industries are simply more valuable to hackers than others. While others may be targeted due to the assumption that they’ll have fewer cyber protocols in place – but with a less lucrative rewards for the hackers.
The big players in highly regulated industries are therefore the most lucrative targets.
The Healthcare Industry
It was found that a staggering 93% of healthcare organizations experienced a data breach between the years 2016 and 2019.
And given that the average cost of a data breach in the healthcare sector costs $7.13 million, it’s clear why the healthcare industry is among the top vulnerable industries to cyber threats.
The top threat faced in the healthcare industry is ransomware and most facilities just aren’t equipped to deal with such attacks.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, cybercriminals took advantage of the increased vulnerabilities in the healthcare industry, doubling the number of data breaches in the year 2019.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are also among the top vulnerable industries to cyber attacks. According to IBM, the average cost of a financial services data breach is a staggering $5.85 million.
Often, cybercriminals target the customers of banks using tactics such as phishing and social engineering.
With a significant pivot towards online banking over the last 5-10 years, there has also been an increase in mobile app trojans. These fake apps impersonate legitimate bank login pages to capture key inputs that a user makes under the pretense they’re on a secure application.
Recent Examples of Cybersecurity Breaches
In 2021 LinkedIn had a data breach that exposed 92% of all members’ personal information – a whopping 700 million users were affected.
It is claimed that the hacker obtained the data by exploiting a LinkedIn API.
Microsoft
Microsoft fell victim to a cyber attack in 2021 that affected more than 30,000 organizations in the USA, including government agencies.
T-Mobile
In 2021, T-Mobile had a data breach that compromised the personal information of more than 48 million users.
Find out more about the applications of AI in cybersecurity by reading our other articles in this cybersecurity series:
