in Intensive Care Units
Early prediction of unusual length of stay (LOS) and in-hospital mortality (IHM) for patients in Intensive Care Units (ICU) can help caregivers identify patients at high risk, and effectively manage their care to prevent adverse events.
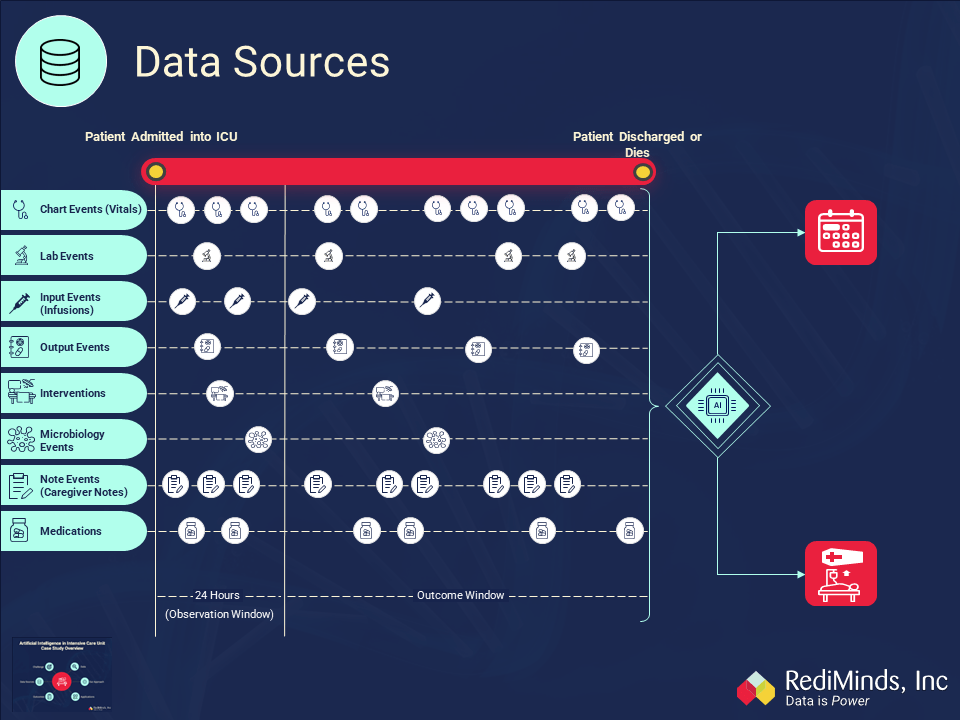
Approach
We utilized Electronic Health Records (EHRs) like chart data, input and output events, laboratory test results, caregiver notes, medications, procedures, imaging reports to build Deep Learning Models (DLMs).
Traditional methodologies for building Machine Learning models utilize a curated set of variables,leaving the majority of data unutilized. In contrast, our approach entailed usage of all digitally-captured patient information from EHRs and other sources.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques were extensively used to synthesize and combine structured and unstructured datasets.
A custom-built deep learning network with input layer, embedding layer, pooling layer, dense layer and output layer was used in the Architecture.
Used scalable cloud infrastructure of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and its tools such as Cloud Storage, Big Query, Tensor Flow, cloud functions and other Artificial Intelligence Platform tools to develop DLMs.
%
AUC-ROC
%
PR-AUC
%
Balanced Accuracy
%
AUC-ROC
%
PR-AUC
%
Balanced Accuracy
In this study, we recognized the potential to develop the next generation of clinical practice tools that can augment the efficiency and effectiveness of caregivers in a critical care setting. However, it is only possible when the data is digitized and ready to be used for model development.
Take a look at how AI algorithms are saving lives affected by hemodynamic instability.
